PD-L1 Testing for Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer Detection
We are proud to offer the validated, semi-quantitative immunohistochemical assay which helps detect PD-L1 protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissue.
About the Test
URMC is one of the only institutions in Western New York to offer this testing to medical oncology professionals using an FDA-approved kit. Add PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx to your lung cancer panel to inform your treatment options for metastatic NSCLC patients. In patients with advanced NSCLC and PDL1 expression in at least 50% of tumor cells, pembrolizumab was associated with significantly longer progression-free and overall survival and with fewer adverse events than platinum-based chemotherapy.*
How it Works
- Assay performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue specimen of at least 100 cells taken from NSCLC patient.
- Assay used to determine PD-L1 expression by IHC.
- Pathologist determines tumor proportion score (TPS) category and numerical TPS.
- Oncologist determines treatment based on TPS number and treatment history.
NSCLC: Analysis for PD-L1 Expression
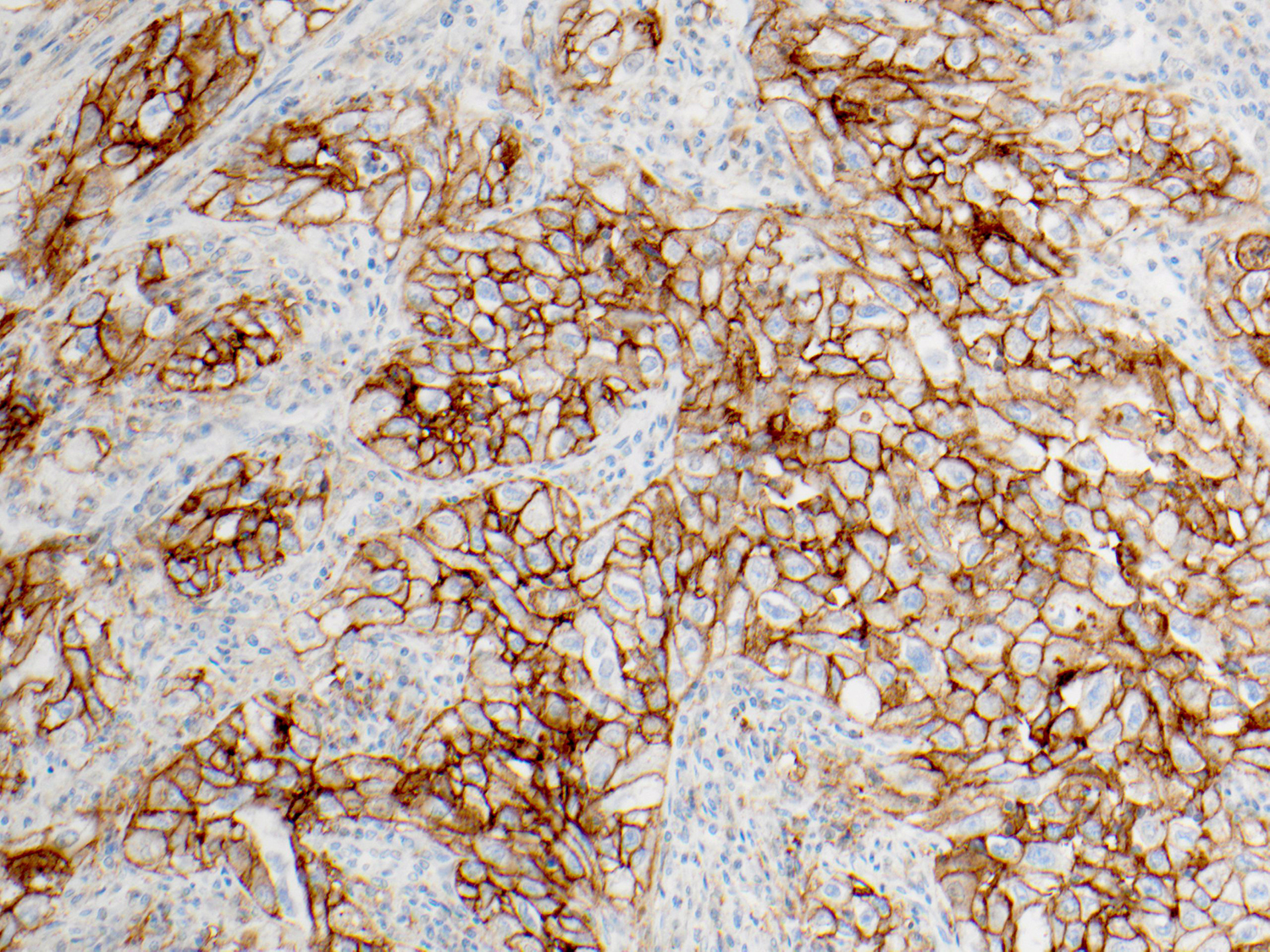
Protein expression is determined using Tumor Proportion Score (TPS), the percentage of viable tumor cells showing partial or complete membrane staining at any intensity. The specimen is considered to have PD-L1 expression if TPS ≥ 1% and high PD-L1 expression if TPS ≥ 50%.
Figure A: No PD-L1 expression (TPS score less than 1%). Patient is not eligible for first or second-line treatment.
Figure B: Low PD-L1 expression (TPS score between 1-49%). Patient is eligible for second-line treatment with pembrolizumab.
Figure C: High PD-L1 expression (TPS score greater than 50%). Patient is eligible for first-line treatment with pembrolizumab.
Contact Us
To learn more or order this test, please call (585) 758-0510.
*References:
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D., et. al; Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. NEJM 2016;375(19):1823.