Pelleting Technique for Subcellular Fraction Electron Microscopy and/or Immunoelectron Microscopy
Subcellular fraction identification of RER, SER, Golgi, mitochondria, peroxisomes, melanosomes, etc. can be examined ultrastructurally using a pellet technique. Purified fractions are pelleted at 150,000 x g for approximately 30 minutes and fixed as a suspension in 2.5% buffered glutaraldehyde for three hours. The pellet is rinsed in buffer, resuspended in a 1:1 (v/v) with 3.0% agarose. This mixture solidifies at room temperature and is processed like a tissue specimen for electron microscopic examination and photography. A variation of this technique is available for immunogold labeling of subcellular fractions.
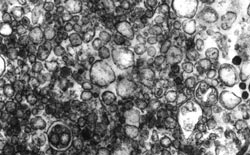
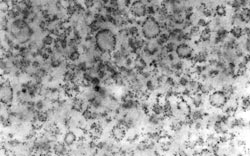
Electron micrograph of smooth (top) and rough (bottom) endoplasmic reticulum (Phung, T.H., Roncome, A., de Mesy Jensen (Bentley), K.L., Sparks, C.E. and Sparks, J. D.: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity is necessary for insulin-dependent inhibition of apolipoprotein B secretion by rat hepatocytes and localized to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 272:30693, 1997.)
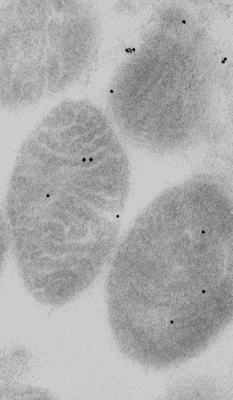
Subcellular fraction of rat heart mitochondria embedded in Lowicryl resin. Sectioned and labelled for ryanodine receptor with 15nm gold tag. (Dr. Gisella Beutner et al, J Biol Chem. 2001. 276(24):21482-8.)