What Are Platelets?
Platelets are tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding. If
one of your blood vessels gets damaged, it sends out signals to the platelets. The
platelets then rush to the site of damage and form a plug (clot) to fix the damage.
The process of spreading across the surface of a damaged blood vessel to stop bleeding
is called adhesion. This is because when platelets get to the site of the injury,
they grow sticky tentacles that help them stick (adhere) to one another. They also
send out chemical signals to attract more platelets. The additional platelets pile
onto the clot in a process called aggregation.
Facts about platelets
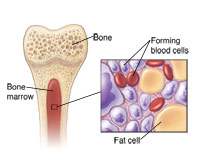
Platelets are made in your bone marrow along with your white and red blood cells.
Your bone marrow is the spongy center inside your bones. Another name for platelets
is thrombocytes. Healthcare providers usually call a clot a thrombus. Once platelets
are made and circulated into your bloodstream, they live for 8 to 10 days.
Under a microscope, a platelet looks like a tiny plate. Your healthcare provider may
do a blood test called a complete blood count (CBC) to find out if your bone marrow
is making the right number of platelets:
-
A normal platelet count is 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood.
-
Your risk for spontaneous bleeding (without being cut) develops if a platelet count
falls below 10,000 to 20,000. When the platelet count is less than 50,000, bleeding
is likely to be more serious if you're cut or bruised.
-
Some people make too many platelets. They can have platelet counts from 500,000 to
more than 1 million.
What happens if your platelet count is high or low
These are health conditions linked to abnormal platelets or abnormal platelet counts:
-
Thrombocytopenia. In this condition, your bone marrow makes too few platelets. Or your platelets are
destroyed. If your platelet count gets too low, bleeding can occur under the skin
as a bruise. Or it can happen inside the body as internal bleeding. Or it can happen
outside the body through a cut that won't stop bleeding or from a nosebleed. Thrombocytopenia
can be caused by many things. These include several medicines, cancer, liver disease,
pregnancy, infections, and an abnormal immune system.
-
Essential thrombocythemia. In this condition, your bone marrow makes too many platelets. People with this condition
may have platelet counts of more than 1 million, which can lead to bleeding, possibly
from platelets being used by forming clots, or from the platelets not functioning
correctly. Other symptoms can include blood clots that form and block blood supply
to the brain or the heart. Healthcare experts don't fully know what causes this type
of thrombocythemia, but changes in bone marrow cells (called mutations) can lead to
some cases.
-
Secondary thrombocytosis. This is another condition caused by too many platelets. Secondary thrombocytosis is
more common. It's not caused by a bone marrow problem. Instead, another disease or
condition stimulates the bone marrow to make more platelets. Causes include infection,
anemia, inflammation, some types of cancer, and reactions to medicines. Symptoms are
usually not serious. People with secondary thrombocytosis have a lower risk of blood
clots and bleeding than those with essential thrombocythemia. The platelet count goes
back to normal when the other condition gets better.
-
Platelet dysfunction. Many rare diseases are linked to poor platelet function. This means the number of
platelets is normal, but the platelets don't work as they should. Medicines, such
as aspirin, can cause this. It's important to know which medicines affect platelets.
Know that while taking these medicines you have an increased risk of bleeding. Always
talk to your healthcare provider before taking new medicine so you understand the
risks and benefits.
Platelets are tiny but important cells in your blood that help your body control bleeding.
If you have symptoms, such as easy bruising, a cut that keeps bleeding, or frequent
nosebleeds, let your healthcare provider know. A simple blood test is all you need
to find out if your platelet count is normal.