Welcome to the Du Lab
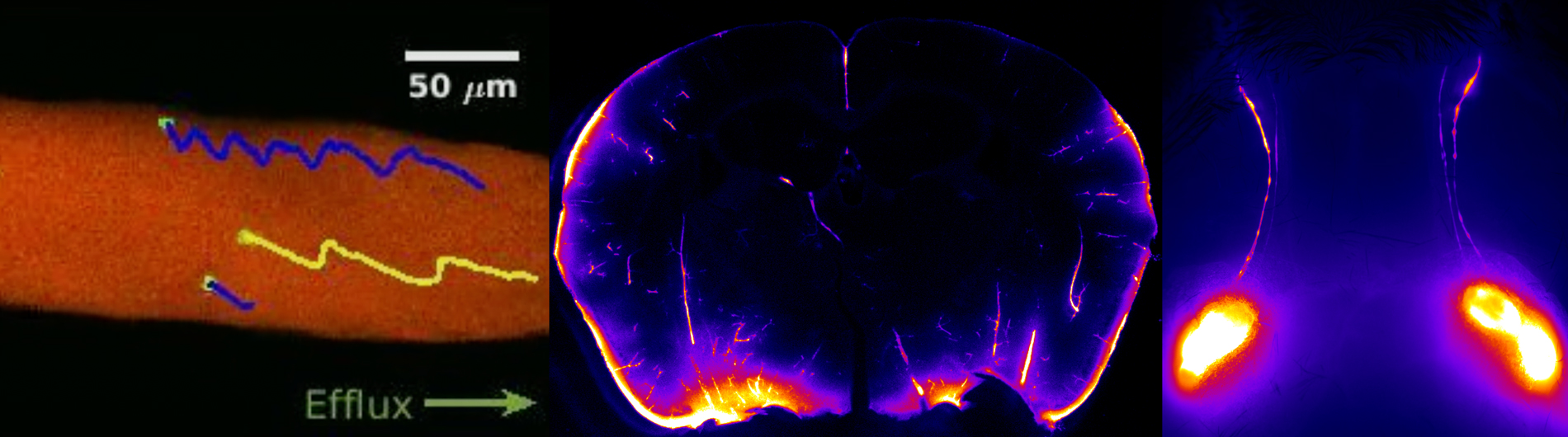
Our lab focuses on "Diseases of Brain Fluid Homeostasis," with the goal of understanding how the brain maintains fluid balance and clears waste to support overall health. We investigate the intricate processes involved in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) production, circulation, and clearance, with a particular emphasis on the role of cervical lymphatic vessels (cLVs) in facilitating brain waste removal. These vessels act as critical pathways for transporting waste-laden CSF to lymph nodes, and their dysfunction can have significant implications for neurological health.
We also study the choroid plexus, a specialized structure that produces CSF, examining how its regulation and dysfunction contribute to conditions such as hydrocephalus, where fluid accumulates abnormally in the brain. Our research extends to exploring the impacts of impaired brain fluid homeostasis in acute and chronic conditions, including stroke and Alzheimer's disease. In Alzheimer's, disrupted fluid clearance is believed to contribute to the accumulation of toxic proteins, such as amyloid-beta, which are central to disease progression.
By combining advanced imaging and molecular biology techniques, our lab seeks to uncover new therapeutic approaches. We aim to identify strategies to restore or enhance brain fluid clearance mechanisms, offering potential treatments for a wide range of neurological disorders.

Ting Du, M.D., Ph.D.
Principal Investigator
Projects
- The function of cervical lymphatic vessels in Alzheimer's disease
- The role of subarachnoid lymphatic-like membrane (SLYM) in traumatic brain injury
- The changes of brain fluid homeostasis in hydrocephalus
Publications
View All Publications- Restoration of cervical lymphatic vessel function in aging rescues cerebrospinal fluid drainage.; Nature aging. 2024 Aug 15.
- Sizes and shapes of perivascular spaces surrounding murine pial arteries.; Fluids and barriers of the CNS; Vol 20(1), pp. 56. 2023 Jul 17.
- Artificial intelligence velocimetry reveals in vivo flow rates, pressure gradients, and shear stresses in murine perivascular flows.; Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America; Vol 120(14), pp. e2217744120. 2023 Mar 29.
- Loss of aquaporin-4 results in glymphatic system dysfunction via brain-wide interstitial fluid stagnation.; eLife; Vol 12. 2023 Feb 09.
- Age- and glaucoma-induced changes to the ocular glymphatic system.; Neurobiology of disease. 2023 Jan 11.
Contact Us
Du Lab
University of Rochester Medical Center
1.9900