

Conditions
We specialize in treating various cardiology conditions such as heart disease, arrhythmias, heart failure, hypertension, and other cardiovascular issues with a personalized, caring approach.
Below is a partial list of the cardiovascular conditions we treat:
Definition
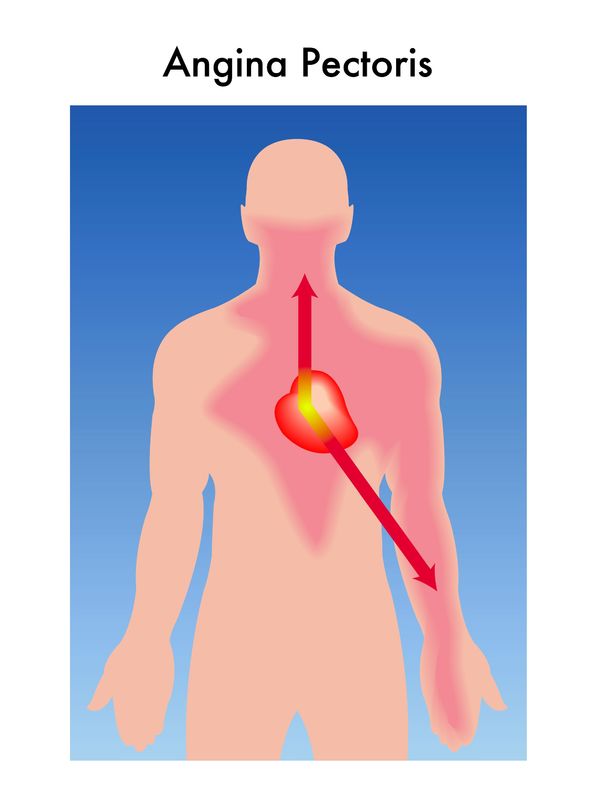 Angina means chest pain, but specifically cardiac chest pain.
Angina means chest pain, but specifically cardiac chest pain.
This is caused by a blockage or reduced blood flow to an area of the heart. Less commonly, angina can be caused by inflammation, spasm of the heart arteries or a tear in one of the heart arteries (dissection).
Symptoms
Angina is a term to describe the sensation felt when there isn’t enough blood flow to the heart itself. Typically, we think of this a intense, center to left-sided pain that is triggered by activity and relieved with rest. Women, however, have less typical symptoms. Less than 60% of women having heart attacks will have a main complaint of chest pain. They more often complain of shortness of breath, fatigue, and/or generalized weakness.
Tests & Preparation
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- You can eat and drink normally prior to the procedure.
- You may take all of your normal medications prior to the procedure.
- You will be asked to remove your pants prior to this procedure.
- We recommend urinating just prior to this procedure so that you are comfortable during the procedure.
Treatments
Treatment depends on the severity. There are medications that control angina, but if symptoms are very severe or are caused by a heart attack, an angiogram (picture of blood vessels) is often needed. If an artery is severely blocked (more than 70%), it can be fixed with an angioplasty, stent, or bypass surgery.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Aortic aneurysm is an abnormal enlargement or bulging of the body’s main blood vessel, the aorta. Aortic aneurysms may lead to serious complications, including rupture, which can be life-threatening if not discovered early.
Risk factors for aortic aneurisms include male gender, age 60 and over, history of smoking, history of aneurysms in other family members.
Symptoms
Most people with aortic aneurisms do not have symptoms. They are usually discovered by doing a screening ultrasound
- Symptoms may include pain in the chest or abdomen.
- Some patients notice a pulsation in the upper part of their abdomen.
- If aneurysms rupture, they are usually very painful and are considered a medical emergency.
Tests & Preparation
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- You can eat and drink normally prior to the procedure.
- You may take all of your normal medications prior to the procedure.
- You will be asked to remove your pants prior to this procedure.
- We recommend urinating just prior to this procedure so that you are comfortable during the procedure.
Treatments
Treatment depends on the size of the aneurysm.
- If the aneurysm is less than 5 cm (or 2 inches) and not growing rapidly, your doctor will probably recommend a repeat ultrasound every 6 to 12 months.
- If the aneurysm is 5.5 cm or larger, surgery to repair the aneurysm is generally recommended because there is higher risk for rupture.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Aortic regurgitation (insufficiency) is a heart condition affecting one of the heart’s major heart valves, the aortic valve. The aortic valve regulates the flow of blood from the main pumping chamber, the left ventricle, to the major blood vessel, the aorta.
When the left ventricle contracts, the aortic valve opens, so blood can flow into the aorta and be delivered to your body’s organs and tissues. The aortic valve then closes, keeping blood from flowing back into the left ventricle.
In aortic insufficiency, the aortic valve does not close normally. This causes blood to leak back into the left ventricle. Over time, this leakage can cause the left ventricle to enlarge and weaken.
Symptoms
- In most instances, patients do not have symptoms. Aortic insufficiency is usually detected when your doctor hears a murmur, or abnormal sound originating from your heart.
- Most common symptoms are usually shortness of breath, especially with activity.
- Other symptoms might include palpitations, a feeling that your heart is pounding, or chest pain.
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram (most common)
- Angiogram or heart catheterization (for some patients)
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
- You will be asked to remove your shirt and bra if applicable, prior to this procedure.
- We recommend urinating just prior to this procedure so that you are comfortable during the procedure.
Treatments
Treatment depends on your symptoms, the amount of regurgitation (or leakage) back into your heart, and the function of the heart muscle.
- People with mild regurgitation and normal heart muscle function generally do not require treatment. Your doctor will recommend follow-up visits to monitor your condition. Your doctor may prescribe medications to help reduce the amount of leakage and lower your blood pressure, if elevated.
- In people with severe leakage who are experiencing symptoms, surgery to replace the aortic valve is sometimes recommended.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm that occurs when the top part of the heart (the atria) are beating at up to 300-600 beats per minute.
As the atria are responsible for being the “pacemaker” of the heart, the atria signal the bottom part of the heart when to beat.
The bottom part of the heart (the ventricles) are responsible for pumping blood to the lungs and to the rest of the body, and when the ventricles beat, this creates our pulse.
In atrial fibrillation, the atria are beating so fast that the ventricles have trouble keeping up, thus the pulse is irregular and occasionally rapid.
Symptoms
- Commonly, patients with atrial fibrillation are asymptomatic
- If a patient has symptoms the most common symptoms are:
- Rapid heart rate
- Irregular pulse
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath (especially with exertion)
- The most concerning side effect of atrial fibrillation is stroke which can occur if the irregular heart rate causes blood to pool and clot inside the heart and then the clot dislodges from the heart and travels to the brain
Tests & Preparation
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
- You will be asked to remove your shirt and bra if applicable, prior to this procedure.
- We recommend urinating just prior to this procedure so that you are comfortable during the procedure.
Treatments
- Heart rate control medications (“antiarrhythmic medications”)
- Blood thinners to prevent strokes
- Aspirin
- Occasionally procedures such as cardioversion or ablation if appropriate
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm in which abnormal electrical signals in the heart’s top chamber (atria) result in a rapid heart beat
Atrial flutter is very similar to atrial fibrillation, another type of heart rhythm disorder. With atrial flutter, blood can pool, leading to small blood clots forming in the heart. These clots can dislodge, travel to the brain, and cause strokes.
Symptoms
- Feeling of your heart racing
- Chest discomfort
- Shortness of breath, especially with physical activity
- Swelling in your legs or feet
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram
- Blood tests to check your thyroid function
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Medicines to slow your heart rate and control its rhythm.
- Blood thinners to prevent clots from forming, which may lead to stroke.
- Cardioversion
- Ablation may be performed if atrial flutter comes back after cardioversion. Although more invasive than a cardioversion, this is generally very safe and effective in restoring the heart’s normal rhythm.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
This is a heart rhythm problem where the heart rate can become abnormally fast — a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). The condition is related to a “short circuit” in the electrical wiring of the heart; there is an abnormal electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles (heart chambers).
Episodes of fast heart rates tend to be brief, usually minutes in duration, but can be longer. AVRT can occur in patients of all ages. It is generally not dangerous (this will not cause a cardiac arrest), but certainly can be associated with very bothersome symptoms. AVRT is not necessarily associated with other heart problems.
Symptoms
- Palpitations; perception of a fast or forceful heart beat
- Chest discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness
Tests & Preparation
- Holter and Event Monitors | Continuous Ambulatory Telemetry
- Electrophysiologic (EP) study; an invasive catheter based procedure where the doctor can “map” out the electrical system of the heart
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Vagal maneuvers (bearing down, forceful coughing) can stop episodes of fast heartbeat
- Medications that slow down the heart rate: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, etc.
- Radiofrequency ablation is most often curative. The procedure involves essentially cauterizing inside the heart at the site of the “short circuit”, and is part of an electrophysiologic (EP) study.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
This is a heart rhythm problem where the heart rate can become abnormally — a fast type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). The condition is related to a “short circuit” in the electrical wiring of the heart; it is in the region of the AV node (part of the normal electrical conduction system of the heart).
Symptoms
- Palpitations; perception of a fast or forceful heart beat
- Chest discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness
Tests & Preparation
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Holter and Event Monitors | Continuous Ambulatory Telemetry
- Electrophysiologic (EP) study; an invasive catheter based procedure where the doctor can “map” out the electrical system of the heart
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Vagal maneuvers (bearing down, forceful coughing) can stop episodes of fast heartbeat
- Medications that slow down the heart rate: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, etc.
- Radiofrequency ablation is most often curative. The procedure involves essentially cauterizing inside the heart at the site of the “short circuit”, and is part of an electrophysiologic (EP) study.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
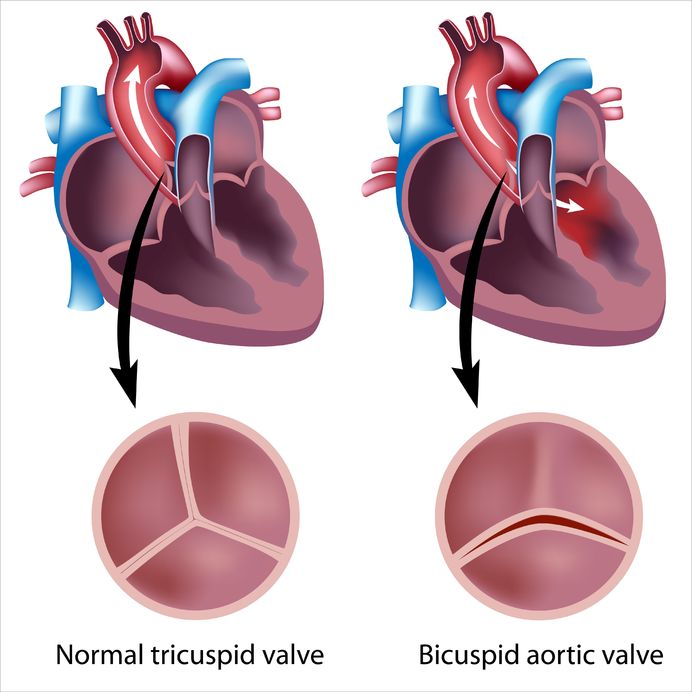
A bicuspid valve is an aortic valve with two leaflets rather than the normal three leaflet valve. This condition can lead to early onset aortic valve stenosis. It can also be associated with leaking of the aortic valve (aortic valve insufficiency) and aneurysms of the aorta.
Bicuspid aortic valve is the most common cardiac valve abnormality which is present from birth with 1-2% of all people having this abnormality. The condition is more common in men than women.
Symptoms
Initially patients are asymptomatic and the abnormality is present from birth. If the valve becomes more significantly narrowed the most common symptoms are
- Shortness of breath with exertion
- Dizziness
- Leg swelling
- Chest pain
- Passing out (syncope)
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram (cardiac ultrasound)
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
No particular medical treatment has been shown to slow progression of the process. Ultimately, affected patients may need valve replacement and/or repair of an aortic aneurysm.
For Additional Information
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
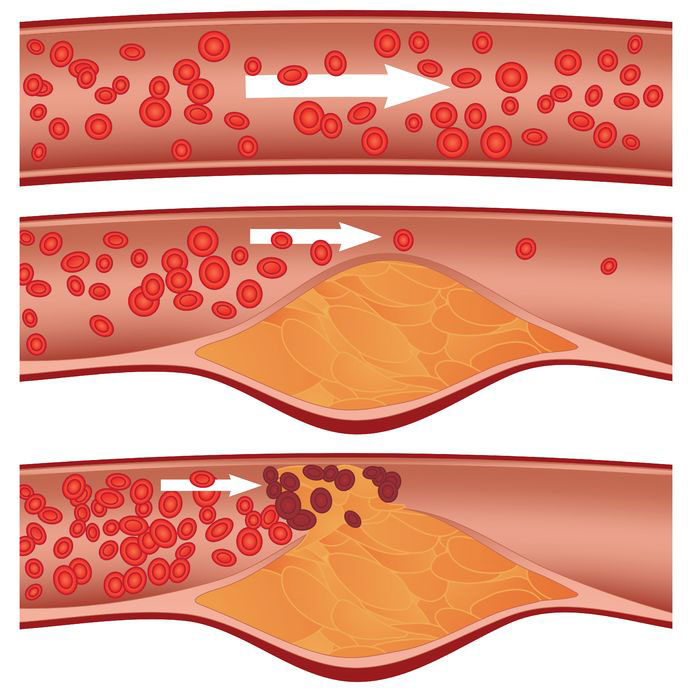
Coronary Artery Disease or Atherosclerosis is caused by cholesterol build up (plaque) in the arteries which supply blood to the heart. The condition is the leading cause of heart attacks due to reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
The disease develops over the course of years, and it is usually caused by eating fatty or fried foods, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, kidney disease, and high blood pressure; however, some patients are genetically predisposed. The more risk factors a person has, the more likely they are to have blockages.
Watch our video about Carotid Artery Stenosis play_circle_outline
Symptoms
- Initially the blockages are asymptomatic until they significantly reduce blood flow to the heart.
- The most common symptom is chest pain/pressure/discomfort (“angina”).
- In some (diabetics, women and elderly patients most commonly), CAD can be asymptomatic.
Tests & Preparation
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Cardiac Stress Test
- Angiogram
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Blood pressure medications (example - metoprolol, lisinopril)
- Cholesterol medications (example - statins [atorvastatin])
- Anti-anginal medications (example - nitroglycerin)
- Aspirin and clopidogrel (Plavix) or ticagrelor (Brilinta)
- Occasionally Stents
- Occasionally Bypass surgery
- Coronary Angioplasty Animation
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Chest pain/discomfort caused by muscle spasm of the muscle within the walls of the coronary arteries (blood supply to the heart muscle)
Muscle spasm causes reduction in blood flow to the heart muscle.
Symptoms
Symptoms are often very similar to pain associated with a more typical heart attack (development of a blockage in a heart artery). Symptoms often occur at rest, and at night. This is different than typical chest pain associated with heart artery blockages which is more typically experience during exertion.
- Chest pressure, heaviness, tightness
- Shortness of breath
Tests & Preparation
- Blood testing to evaluate for heart muscle inflammation/damage; usually ordered in conjunction with presentation to the emergency department
- A cardiac stress test or angiogram are often required to rule out significant blockages in the coronary arteries
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Medications that relax the muscle in the arteries can prevent spasm
- Examples are calcium channel blockers and nitroglycerin type medications
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Edema is swelling, reflective of fluid retention in and underneath the skin. The condition may be associated with:
- Medical problems where the protein levels in the body are low, which can lead to fluid “leaking” out of the blood vessels
- Problems with the veins such as blood clots, leaky valves in the veins, or increased pressure on the veins.
- A heart problem
Edema can accompany many illnesses or surgeries that require patients to receive significant amounts of IV fluid.
Symptoms
- Pain, redness at site of edema
- Shortness of breath
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram
- Vascular Ultrasound
- Blood tests
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Elevation of the legs when seated
- Compression stockings
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Evaluate for underlying causes that can be treated.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
The chest is a complex area in the body, and many organs reside behind the breast bone. When we have pain in the chest, we usually think of the heart, but pain can also come from the muscles, the lungs, the sac around the heart, and or the digestive system.
The esophagus sits directly behind the heart and can cause chest pain. This is usually the result the reflux of acidic particles from the stomach upwards into the esophagus. These particles can cause the esophagus, which has muscle in it, to spasm
Symptoms
- Patients usually feel a chest tightness after meals or when laying flat
- Discomfort can last for more than 20 minutes
Tests & Preparation
- Testing is usually a trial of certain medications to see if they reduce the pain
- Sometimes, an endoscopy is used to get clues. Endoscopy is procedure where a camera is inserted into the esophagus to look at it directly and take samples of the tissue
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
Medications are the mainstay of treatment. There are multiple medications available. Some suppress the formation of acid in the stomach, and others relax the muscle in the esophagus.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Heart failure means that the heart isn't pumping as effectively as it should. Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle weakens and is unable to circulate enough blood to meet the body's needs, often causing shortness of breath, fatigue and leg swelling. When fluid builds up, the condition is called congestive heart failure.
Heart failure usually develops slowly, often as a result of an underlying heart condition, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, damaged heart valves, a congenital heart defect or arrhythmia. Heart failure may also arise as a complication of a heart attack.
The term "heart failure" makes it sound like the heart is no longer working at all and there's nothing that can be done. Heart failure is a serious condition, but many people with heart failure lead a full, enjoyable life when the condition is managed with medication and healthy lifestyle changes. It's also helpful to have the support of family and friends who understand your condition.
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Leg swelling
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
Although heart damage is often irreversible, many heart failure treatments can strengthen the heart and improve symptoms.
- Medications like ACE inhibitors and diuretics to treat high blood pressure and congestive heart failure can help patients live longer and more comfortably.
- Those with more severe cases of heart failure may benefit from surgery to repair damaged heart valves or unclog arteries.
- Healthy lifestyle changes
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Hyperlipidemia, or high cholesterol, refers to increased levels of lipids, or fats, in the blood. This can cause a build up of plaque in the walls of your arteries and reduce the supply of oxygen to your heart. Hyperlipidemia may increase your risk of heart attack, stroke, or peripheral vascular disease.
Symptoms
- Most people with hyperlipidemia have no symptoms.
- Build up of plaque in your arteries may lead to symptoms of heart attack (chest pain, difficulty breathing), stroke or TIA (speech difficulty, weakness or numbness on one side of your body), or claudication (pain in your calves, thigh, or buttocks with walking).
Tests & Preparation
Hyperlipidemia is diagnosed by a simple blood test, done after you have been fasting at least for 12 hours. The test includes measurement of your total cholesterol, the LDL or “bad cholesterol”, and HDL or “good cholesterol”. In general, the goals for your cholesterol should be
- Total cholesterol of less than 200,
- Good cholesterol (HDL) above 50
- Bad cholesterol (LDL) below 130
Patients with certain conditions, including a history of heart attack, stroke or aortic aneurysm should have even stricter goals for their cholesterol.
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
Treatment of high cholesterol depends on your risk of developing heart disease. Your doctor will recommend a healthy diet low in cholesterol and saturated fat. Your doctor may also recommend medicine to help lower your cholesterol to reduce your risk of stroke or heart attack. Factors that we take into consideration include:
- Your individual cholesterol numbers, including the amount of “good” and “bad” cholesterol
- The presence of other health conditions such as heart attack or stroke
- The presence of other risk factors for heart disease such as smoking, diabetes, or high blood pressure
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy (HOCM) is a cardiac abnormality which leads to the muscle in the wall of the heart growing and thickening to the point that it blocks blood flow exiting the heart.
- During periods of strenuous exertion and/or dehydration, the degree of obstruction to blood flow progresses and can prevent the heart from pumping blood to the rest of the body, including the heart itself. This can then cause heart rhythm abnormalities, cardiac arrest (the heart stops) and death. HOCM is the leading cause of sudden cardiac death in athletes.
Watch our video about Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy (HOCM) play_circle_outline
Symptoms
- Often, this condition is asymptomatic until someone passes out or suffers cardiac arrest, unfortunately.
- If a young person is having dizziness, chest pain or passes out during exercise, this condition should be considered.
Tests & Preparation
- Physical exam
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Echocardiogram
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Sometimes patients will be placed on drugs such as beta-blockers (metoprolol, atenolol, etc) to prevent heart rhythm abnormalities and to relax the heart.
- Patients may require surgery or a cardiac catheterization procedure (angiogram) to remove the excess muscle tissue in the heart.
- This problem may require implantation of a defibrillator to prevent life-threatening arrhythmias.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition

Cardiomyopathy refers to a condition in which the heart muscle is weakened and not able to maintain normal circulation of your blood.
The most common complication of ischemic cardiomyopathy is congestive heart failure. This is a condition in which fluid builds up in the lungs and feet, causing swelling and difficulty breathing.
Watch our video about Ischemic Cardiomyopthy play_circle_outline
Symptoms
- Chest discomfort, or angina, due to lack of oxygen to your heart muscle.
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling in your feet or ankles
Tests & Preparation
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) This a test measuring electrical activity of the heart, and may help determine if you’ve suffered a previous heart attack
- Echocardiogram This uses sound waves to measure your heart function.
- Angiogram. This is done by your doctor inserting a narrow hollow tube into a large artery in your leg or arm and directing the tube up to your heart. X-ray dye is then injected through the tube, allowing your doctor to look for blockages in the vessels supplying blood to the heart.
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Medications called diuretics are prescribed to remove extra fluid in your lungs, making it easier for you to breathe.
- Other medications may be prescribed to help strengthen the heart muscle.
- Procedures to improve blood flow to the heart muscle. This may include angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Non-Ischemic cardiomyopathy is a generic term which includes all causes of decreased heart function other than those caused by heart attacks or blockages in the arteries of the heart.
The most common causes of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy are viral infection (viral myocarditis), drug reactions, inflammation or autoimmune reactions (lupus myocarditis, etc) or infiltrative processes (sarcoid, amyloid, etc).
Normal heart function, or ejection fraction (EF), is 55-65%. This means that with each beat, the heart pumps 55-65% of the blood inside the heart to the rest of the body. Cardiomyopathy implies some decrease in EF to less than 50% (which is considered borderline or low normal.)
Watch our video about Non-ischemic Cardiomyopathy play_circle_outline
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Edema or swelling
- Fatigue, especially with exertion
- Unexplained weight gain
- Shortness of breath when lying down
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac Stress Test (occasionally)
- Angiogram (rarely)
- Some blood tests may be helpful in making the diagnosis
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Beta-blockers (atenolol, metoprolol, carvedilol, etc) can relax the heart, lower blood pressure and slow the heart to improve filling and pumping function.
- Medications classified as ACE-inhibitors (lisinopril, enalapril, etc) or ARB’s (losartan, candesartan, etc) can also lower blood pressure, relax the heart and improved blood flow to the kidney.
- Diuretics may be used to remove excess fluid.
- Spironolactone can also be used to remove fluid and help relax the heart.
- Pacemakers or defibrillators may be recommended in some cases.
- Other treatments may be considered depending on the cause of the cardiomyopathy.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
This is a small hole between the top two chambers of the heart (the atria).
This condition occurs in approximately 15% of all people.
Usually undetected, if the hole is large enough, it can lead to blood with oxygen mixing with blood that has not yet received oxygen from the lungs. Can also cause pressure overload on the right side of the heart due to shunting of blood from the higher pressure left atrium into the lower pressure right atrium.
Watch our video about Patent Foramen Ovale play_circle_outline
Symptoms
- Usually these are asymptomatic and found accidentally on cardiac ultrasound.
- There is some evidence that there may be a higher association of stroke in patients with PFO/ASD’s.
- There is weak evidence of association of PFO/ASD with migraine headaches.
Tests & Preparation
- Echocardiogram
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Usually no treatment is needed.
- If a patient has had a stroke and they have a PFO/ASD they likely should be on aspirin daily.
- Rarely, closing the hole with a catheter procedure may be warranted, but usually this is unwarranted.
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Premature Ventricular Contractions, or PVCs, are “extra” heart beats that start in the lower portion of the heart. The normal pathway is top-to-bottom.
Nearly all of the 100,000 beats that occur each day start from the top part of the heart named the atria. The atria holds the “pacemaker” cells, which set the rate.
Every heart cell has the ability to start a beat and PVCs do just that, reversing the pathway from bottom-top. These are typically self-limiting or only treated if symptoms are bothersome. In some cases, the condition may be reflective of underlying structural disease.
Watch our video about Premature Ventricular Contractions play_circle_outline
Symptoms
- Patients typically described “skipped beats” or palpitations in the chest
- Lightheadedness, passing out spells, or chest discomfort
Tests & Preparation
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Holter and Event Monitors | Continuous Ambulatory Telemetry
Treatments
The first step is to find out how many Premature Ventricular Contractions are occurring.
- An ultrasound is typically performed to rule out structural heart disease
- An attempt is made to identify and remove possible triggers (caffeine, alcohol, stress, tobacco, energy drinks, some inhalers)
- Beta blockers are medicines that are the treatment of choice for most cases
- In very rare instances more aggressive medications or ablations are necessary
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.
Definition
Type of arrhythmia (irregular heart rhythm) occurring in the top chambers (atria) of the heart.
Generally benign. Can last seconds to years.
Encompasses a variety of rhythms including – PACs, PSVT, Accessory tract tachycardias, AVNRT, AVRT, atrial tachycardia, Atrial Fibrillation, and Atrial Flutter.
Symptoms
- Commonly cause palpitations
- Can cause lightheadedness, dizziness, and rarely cause syncope
- Generally the degree of symptoms is related to the length of symptoms
Tests & Preparation
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Echocardiogram
- Holter and Event Monitors | Continuous Ambulatory Telemetry
- EP (electrophysiology) testing
- Cardiac Stress Test
What Preparation is Required Prior To This Procedure
- There is no particular preparation needed prior to this procedure.
- You should take all of your normal medications as prescribed before this procedure.
Treatments
- Monitoring or watchful waiting
- Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers
- Anti-arrhythmic medications
- Ablation (radiofrequency ablation)
Next Steps
If this condition is Interfering with your everyday life, Contact us for a consultation with our of our board certified and fellowship trained cardiologists.