Welcome to the RNA Processing Lab
Molecular Mechanism of RNA Processing as it Relates to Human Disease
While decades of research have focused on how transcription initiates, a current and exciting focus is now to determine how RNA polymerase terminates at genes. All genes that produce either coding or noncoding transcripts must form the 3' end of RNA through the process of termination. The molecular mechanism of polymerase termination is only beginning to be understood, but it is clear that termination is subject to regulation and is highly dynamic. Any disruption in proper termination leads to dysregulated gene expression that is observed in multiple human disease contexts including cancer and developmental disorders. Thus, through understanding of the molecular process of termination, better and tailored therapeutics can be designed and tested.
My laboratory is focused on understanding and characterizing the process of termination in eukaryotes. Specifically, we are interested in how the 3' end of RNA is formed at the terminus of both coding and noncoding genes. Research projects in my laboratory will use a blend of classical biochemical and molecular biological techniques coupled with an extensive array of next-generation sequencing approaches and use of functional genomics. Our ultimate goals are to decipher how molecular machines regulate termination, how these machines fail in human disease, and to leverage that knowledge for the creation of therapeutics.

Eric J. Wagner, Ph.D.
Principal Investigator
Special Announcement
Projects
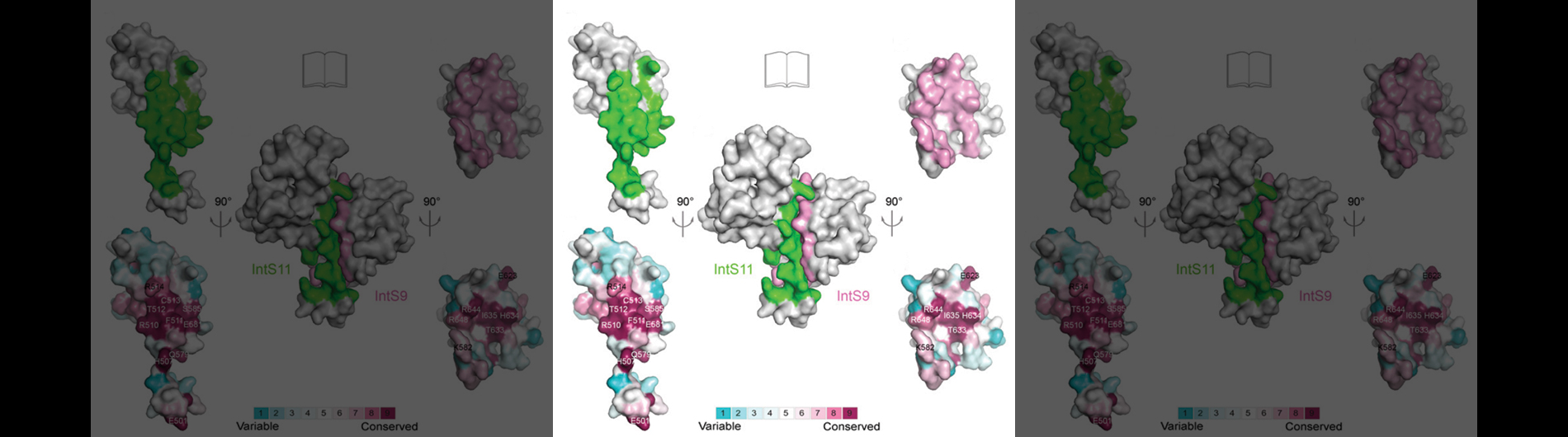
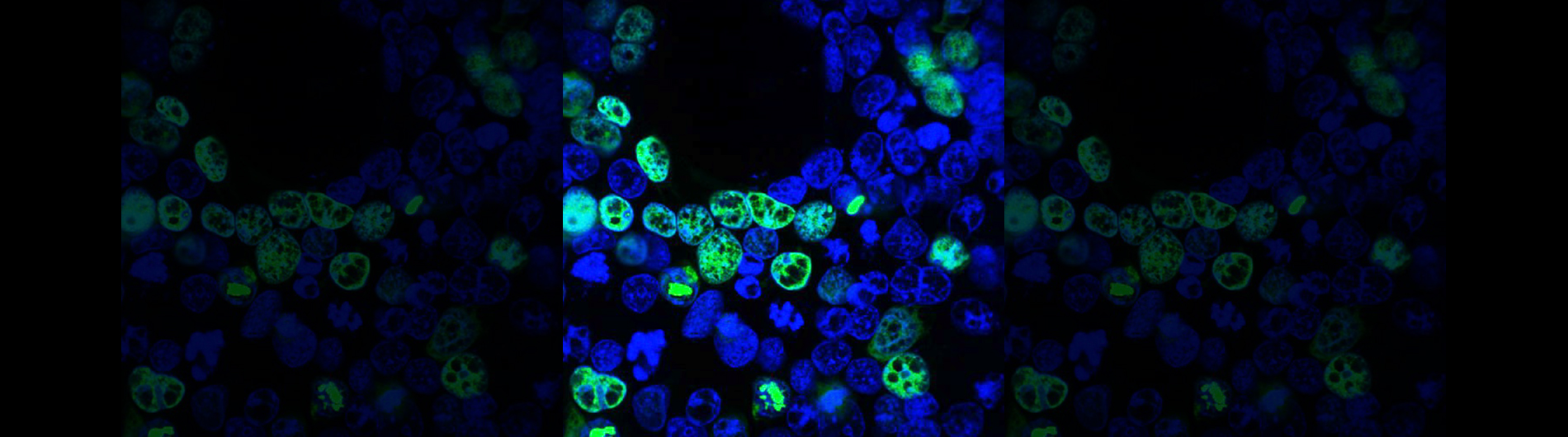
The Role of the Integrator Complex in Gene Expression Regulation
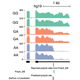
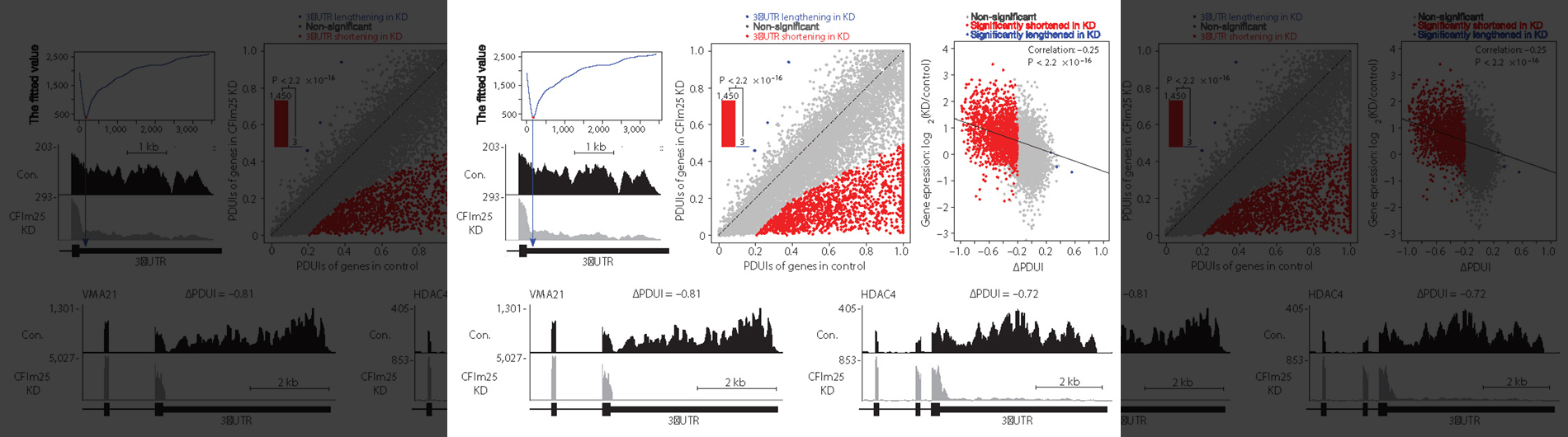
Alternative Polyadenylation in Cancer and other human disease settings
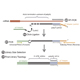
Use of PolyA-Click-seq (PAC-seq) to investigate disease relevant gene expression and alternative polyadenylation
Publications
View All Publications- HIV-1 infection regulates gene expression by altering alternative polyadenylation correlated with CPSF6 and CPSF5 redistribution.; mBio. 2025 Dec 17.
- HIV-1 Infection Regulates Gene Expression by Altering Alternative Polyadenylation Through CPSF6 and CPSF5 Delocalization.; bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology. 2025 Aug 07.
- Integrator loss leads to dsRNA formation that triggers the integrated stress response.; Cell. 2025 Apr 10.
- Cytoplasmic binding partners of the Integrator endonuclease INTS11 and its paralog CPSF73 are required for their nuclear function.; Molecular cell. 2024 Jul 08.
Contact Us
Wagner Lab
KMRB G.9852
601 Elmwood Ave
Rochester, NY 14642