PEG
Corflo Percutaneous Endoscopy Gastrostomy Tube (PEG Tube; Non-balloon G-tube)
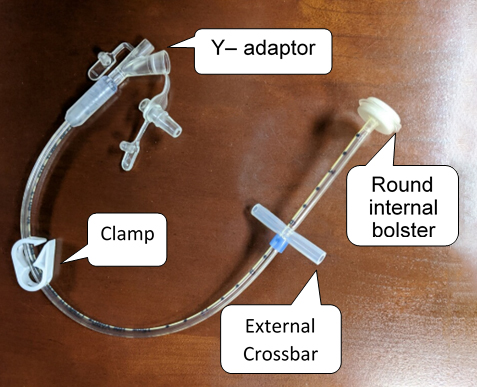
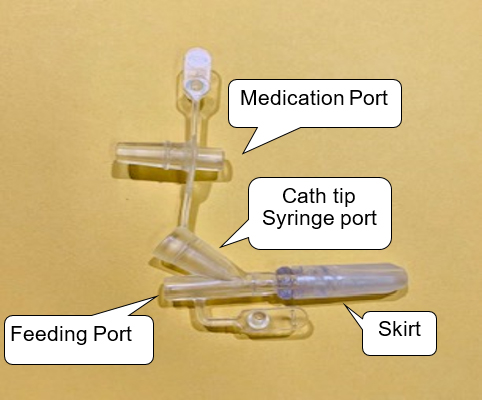
This is a long clear tube that is placed into the stomach during surgery. During the procedure, your child’s surgeon will place an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera and light at the tip) through your child’s mouth into their stomach to guide the G-tube placement. The PEG tube will have two ports at the end of the tube: a feeding port and a separate port for medications. The Y-adaptor end of the tube can be easily replaced if it gets worn out. In general, the PEG tube will remain in place for a minimum of 4-6 months after surgery. If the PEG tube is replaced in the future, your child will not need another surgery but will need sedation for the tube change.
Caring for the PEG (Non-Balloon) Type Gastrostomy Tube and Site
Cleaning the Site
- Wash your hands with soap and water before touching the G-tube site.
- Use warm soapy water on a Q-tip to clean around the G-tube once a day (more often if needed).
(May use ½ strength hydrogen peroxide instead if there is crusting around the tube that is difficult to remove with soap and water or if it is becoming reddened around the tube. If using ½ strength hydrogen peroxide be sure to rinse with plain water after cleansing.) - Pat dry.
- After 2 weeks from original tube placement/surgery, may have regular baths (submerge in water)
- Do not use heavily scented soaps or cleansers.
- Do not apply ointments or medications to the area unless instructed by your healthcare provider
Dressing
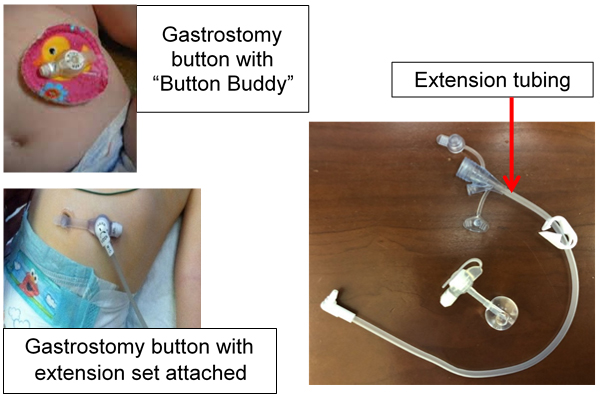
- Keep a split gauze around the tube at all times. (You should not use a button buddy with this type of tube)
- Change it daily or when it becomes soiled/moist
- Be sure to turn the tube in the tract at least once daily (about ¼ of a turn) to avoid the external bar from irritating the skin in the same spot.
Securing the Tube
Movement and pulling on the G-tube site should be minimized to prevent trauma and leakage.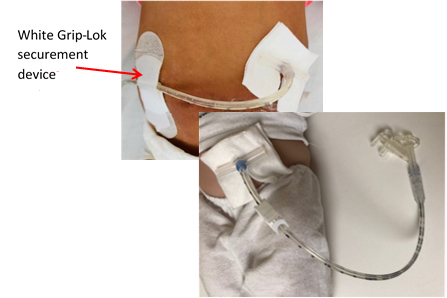
- You should always use some sort of securement device, such as a Grip-Lok or Cinch, or medical tape, such as Micropore (paper tape) or Hypafix, to secure the length of this tube.
- Onesies, one-piece sleepers, overalls, or other one-piece clothing will help keep the G-tube from being pulled out.
- Stretchy gauze/netting used to cover abdomen
- ACE bandage: May be used similar to an abdominal binder for younger children/infants. If using ACE wrap, cut it in half (across the width of the ACE) and be sure not to pull it tightly around the abdomen or it will compress the G-tube into your child’s skin
- Abdominal binder: may be used for older children/adolescents
- Use a “tape tag” and safety pin to pin the tube to your child’s clothing to prevent accidental pulling at the G-tube site. (If using, be careful when undressing your child. You MUST remove the safety pin first!)
Bathing and Swimming
- May swim in a chlorinated pool 2 weeks after surgery as long as the exit site is well healed
- May swim in a lake/ocean 2 months after surgery
Activity
- Your child may not participate in strenuous activities (contact sports, gym class, playground equipment, etc) for 1 month. After 1 month, your child may participate in strenuous activities if they keep the G-tube covered/secured (minimally for the first 3 months) to prevent dislodgement. After 3 months, your child should remain mindful of the G-tube, but a abdominal binder/cover is not required.
- Tummy time is okay. Your child may sleep or spend time on his belly. Make sure the G-tube is taped securely.
- If your child does physical therapy/occupational therapy, they may resume 2 weeks after surgery. Until then they may also do exercises that do not place them on their belly or use core muscles.
Using the PEG (Non-Balloon) Type G-Tube
Giving Medications or Flushing a PEG G-Tube (long clear tube, no balloon)
Supplies needed: medications in liquid form, water for flushing, catheter tip or oral syringe
- Fill syringe with water (amount to be determined by your health care provider)
- Open the cap on the medication port or feeding tube port at the end of the G-tube and attach the tip of the filled syringe
- Slowly push the water into the tube.
- If no issues flushing the tube, may repeat process with the medications. Be sure to clamp the tube between each medication and flushes to prevent leakage of medications/flushes.
- Flush the tubing with water after giving medication.
- Cap the tube if not in use.
Feeding Through a PEG G-Tube (long clear tube, no balloon)
Supplies needed: Feeding pump, feeding pump tubing/bag, IV pole, formula at room temperature.
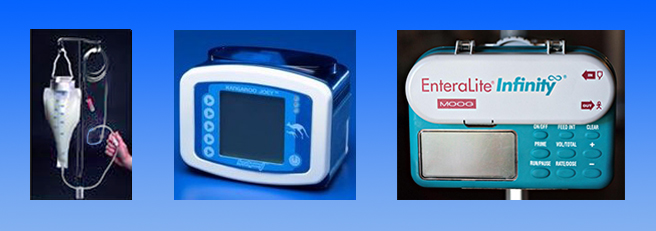
- Hang feeding bag on IV pole.
- Fill feeding bag with formula. (No more than 8 hours of formula at a time).
- Place tubing into the pump. Prime tubing (run the formula through the tubing) as instructed.
- Set the pump settings as instructed
- Clamp the tube to prevent leakage
- Connect pump tubing to the G-tube feeding/medication port.
- Start the pump, making sure to unclamp the G-tube extension set.
- Once the feeding is completed, flush the G-tube as instructed, and rinse feeding bag and tubing with warm tap water.
- Discard or wash the feeding bag and tubing every 24h or as instructed
Venting a PEG G-Tube (long clear tube, no balloon):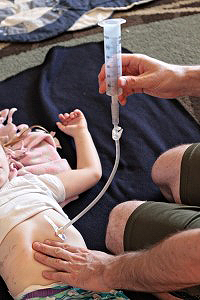
- Venting is done to release air from the child’s stomach (when the child’s belly looks big/distended, the child seems uncomfortable, or the child needs to burp)
- Place a 60mL catheter tip syringe without the plunger on the end of the G-tube (on the feeding/medication port)
- Unclamp the G-tube
- Allow air to come out through the tube into the syringe (1 – 2 Minutes).
- If air does not come out… clamp the G-tube, remove the syringe, place the plunger back into the syringe.
- Then place syringe with plunger into the G-tube feeding/medication port.
- Unclamp the G-tube and pull back gently on the plunger to get the air out of the child’s stomach.
- Formula may come back into the syringe during venting, be sure to give any formula that backs up in the syringe back to the child taking care not to push in any air.
- Once you are done clamp the G-tube, remove the syringe and cap the end of the G-tube.
Cleaning the Equipment
- Wash feed tubing with warm soapy water or half white vinegar/half water solution
- Flush tube through with warm water
- Hang to dry or flush air through tubing
- May reuse tubing for 2 weeks
- Rinse feeding bags after use
- Do not put tubing in the dishwasher
Changing the PEG (Non-Balloon) Type G-tube
Your child’s surgeon will decide when your child’s PEG tube should be replaced. There are a couple options for replacement tubes.
MIC Gastrostomy Tube (long, balloon type tube)
Long clear tube with markings along the tubing, a silicone bolster (plastic disk) outside, and a balloon inside. This tube does not need to be replaced surgically and can be changed at home or in the office. There are 3 ports at the end of the tube: a large clear port for feedings, a small clear port for medications, and a numbered (white) port which is the balloon port. There is not a clamp on this tube; instead you must kink/pinch the tubing to prevent leakage.

Low profile balloon tube (MIC-KEY or AMT Mini-ONE Button)
Skin level tube with a balloon inside the stomach. Additional tubing can be attached to the button to give feedings, medications and to vent the stomach if needed.